
The onset of cavities in children can occur as soon as the first tooth emerges, making it a possibility that should not be underestimated. Despite the potential, the likelihood of tooth decay in very young children is higher than one might assume. Recent data from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research reveals that approximately 28% of American children aged 2 to 5 already have cavities.
Compounding the issue, tooth decay in very young children tends to be particularly aggressive. Left untreated, it can swiftly lead to the complete destruction of teeth and give rise to infections, escalating into medical emergencies. This poses a significant challenge, as tooth decay often remains unaddressed in very young children. In fact, a study found that around 52% of children aged 3.5 years or younger, presenting caries-related emergencies at a U.S. children’s hospital, had their first encounter with a dentist in the emergency room.
To safeguard your child against early childhood caries, it is crucial to understand the disease and take preventive measures.
What Is EEC (Early Childhood Caries)?
Early childhood caries (ECC), is referring to tooth decay in children under the age of six, it is identified if the child currently has a decayed tooth, has lost a tooth due to decay, or has had a cavity filled.
What Does Tooth Decay Look Like in children?
Recognizing the appearance of tooth decay in babies, toddlers, and preschoolers is essential. In its early stages, tooth decay manifests as small white or brown spots on children’s teeth, progressing into small holes (cavities) as the disease advances. If untreated, the decay can ultimately destroy most or all of the affected tooth’s crown, leaving only a small stump above the gumline.
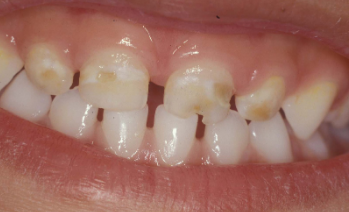
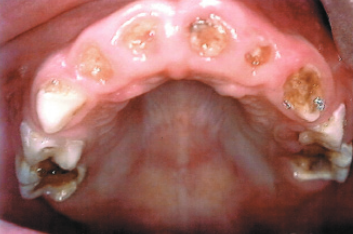
What Is the Difference Between baby bottle tooth decay and Early Childhood Caries?
Distinguishing early childhood caries from baby bottle tooth decay is primarily a matter of nomenclature. Previously referred to as “baby bottle tooth decay” or “nursing caries,” the term has evolved to “early childhood caries” to better reflect the multifaceted causes of tooth decay in very young children, extending beyond feeding practices.
How is tooth decay in childrent Treated?
Addressing cavities in baby teeth involves appropriate treatment depending on the disease’s progression. Minor cavities may be treatable with a dental filling, while deeper cavities may require pediatric pulp therapy or even extraction. In cases where cavities are in the early stages, before becoming cavitated, non-invasive treatment plans may include fluoride varnish treatments, dietary modifications, and improved oral hygiene practices.
What Happens If You Don’t take are of tooth decay in baby teeth?
Neglecting the treatment of early childhood caries can have serious consequences. Cavities in baby teeth, if left untreated, can lead to pain, premature tooth loss, and severe infections. The pain associated with cavities can be intense, affecting the child’s sleep and potentially spreading to the dental pulp, resulting in severe infections. Premature tooth loss can lead to long-term dental issues, including misalignment and bite problems. Moreover, serious infections from untreated cavities can extend beyond the dental area, posing risks such as brain abscesses and Ludwig’s Angina.
Tooth decay in children also referred to as dental cavities or caries, stand as the most common chronic disease of childhood in the US. Neglected cavities have the potential to induce pain and infections, impacting essential activities such as eating, speaking, playing, and learning. Consequently, children with compromised oral health tend to experience increased school absences and lower academic performance compared to their counterparts with better oral hygiene.
How to Prevent tooth decay in children
To prevent early childhood caries, it is essential to understand its causes and adopt preventive measures. Seeking additional information on cavity prevention in children can provide valuable insights into protecting your baby or child from developing cavities.
Tooth decay in children is the most chronic childhood disease in the United States

Are you looking for a dental home for your child? Call us to schedule an appointment!
Call us and schedule your child’s appointment today: (702)586-4347
Are dental x-rays safe for my child?
Are dental x-rays safe for my child? The most common...
Read MoreDoes my child need a mouthguard for sports?
Does my child need a mouthguard for sports? Are you...
Read MoreDental tips for kids during Summer break
Dental tips for kids during Summer break The summer sun...
Read More




